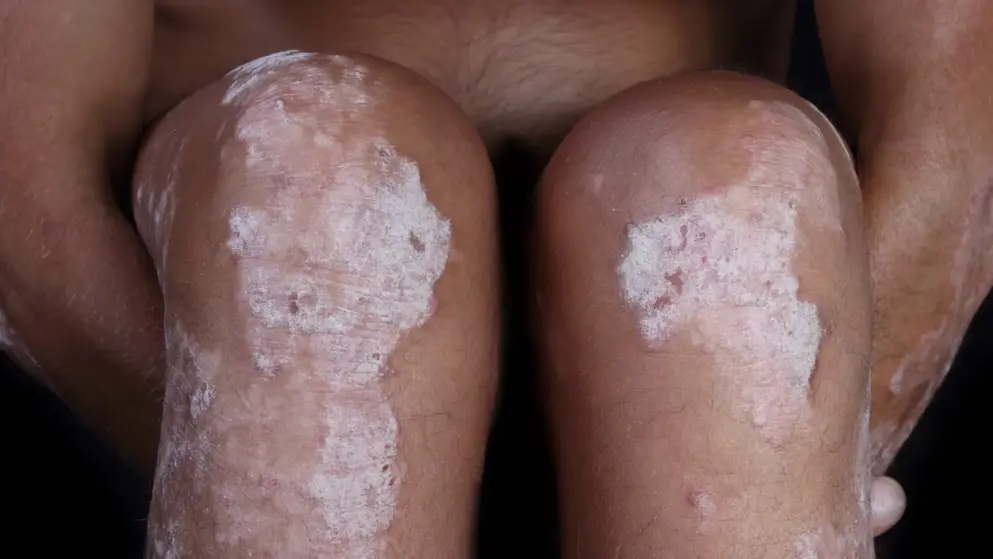
NICE gives positive recommendation of Skyrizi for psoriasis in final guidance
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has published a positive Final Appraisal Document (FAD), confirming that Skyrizi (risankizumab), from AbbVie, is recommended for the treatment of severe psoriasis in adult patients who have failed conventional systemic therapies. Risankizumab is part of a collaboration between Boehringer Ingelheim and AbbVie, with AbbVie leading development and commercialisation globally. In clinical studies, risankizumab demonstrated high rates of skin clearance at 16 weeks and this clearance was also maintained through to one year (52 weeks).
The NICE FAD is based on results from four pivotal Phase III studies, UltIMMa-1, UltIMMa-2, IMMvent and IMMhance evaluating more than 2,000 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Across all four studies, the co-primary endpoints were at least a 90 percent improvement in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 90) and a static Physician Global Assessment (sPGA) score of clear or almost clear (sPGA 0/1) at week 16.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were upper respiratory infections, which occurred in 13 percent of patients. Common adverse reactions (frequency defined as greater than or equal to 1/100 events to less than 1/10) included tinea infections, headache, pruritus, fatigue and injection site reactions.