Noveartis initiates ARROW study to assess Cosentyx over Tremfya in psoriasis patients.
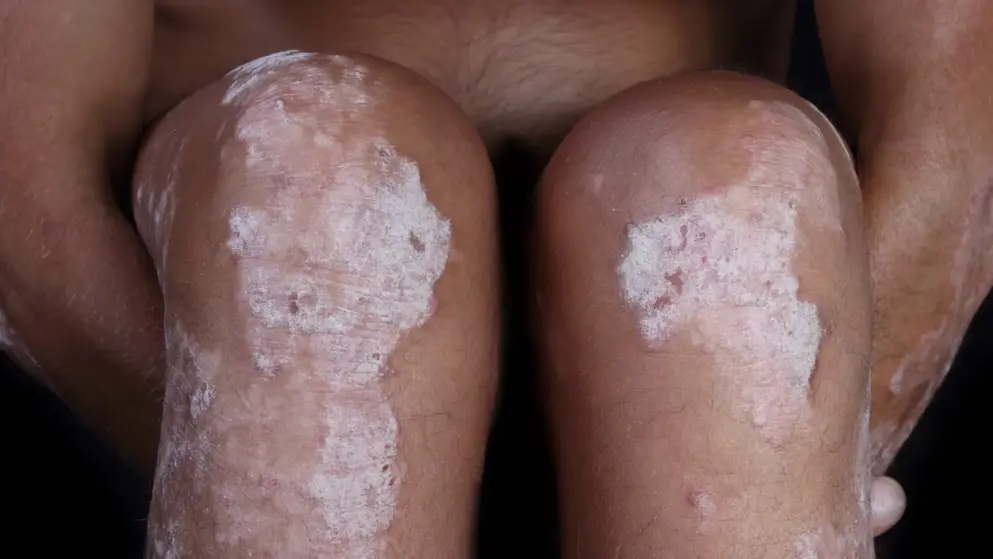
Novartis announced the plan to initiate ARROW, a head-to-head proof of concept study to assess the mechanistic superiority of the direct inhibition of IL-17A with Cosentyx (secukinumab) over the inhibition of IL-23 with Tremfya (guselkumab) in patients with psoriatic plaques resistant to treatment with Stelara . Study results are expected in 2019.
The ARROW study objective is to assess the mechanistic superiority of Cosentyx over Tremfya in controlling clinical activity in psoriatic plaques resistant to treatment with Stelara . IL-23 independent pathways of IL-17A release are potentially involved in inflammation of other persistent localizations, including joints, scalp, nails, palms and soles psoriasis. Up to 90% of people with psoriasis may develop nail or palmoplantar psoriasis. Nail psoriasis is an important predictor of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) which affects up to 40% of patients with psoriasis.
Cosentyx is the first fully-human biologic that specifically inhibits interleukin-17A (IL-17A), a cornerstone cytokine involved in the inflammation and development of psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). IL-17A is produced by both IL-23 dependent and IL-23 independent pathways, by various cells from both the innate immune system (which can be triggered by mechanical stress) and the adaptive immune system. By acting directly on IL-17A, Cosentyx inhibits this cornerstone cytokine irrespective of where the IL-17A comes from.