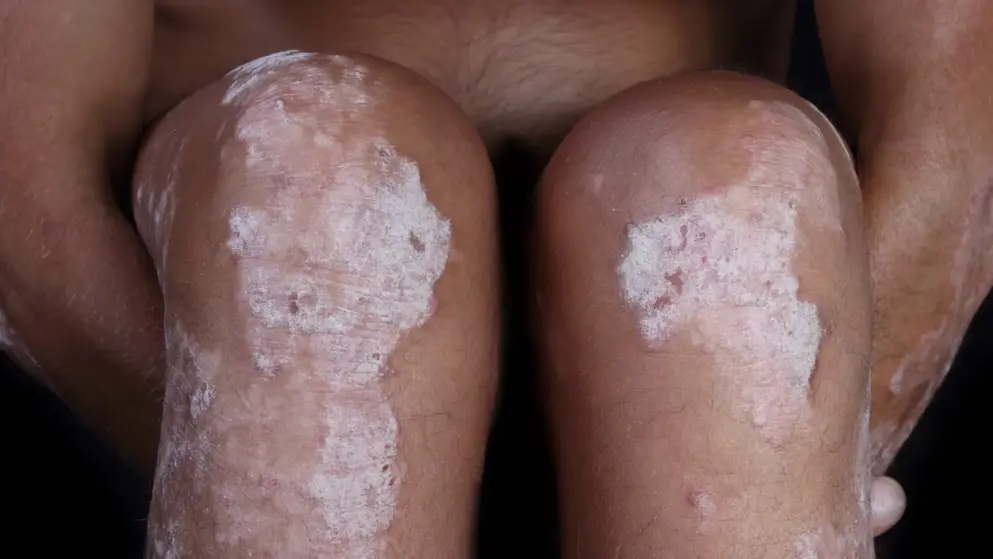
Janssen reports VOYAGE 2 and NAVIGATE Phase III studies of guselkumab (CNTO 1959) for treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis.
Janssen Research & Development, LLC (Janssen) announced new findings from two pivotal Phase III studies reporting the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Data from the VOYAGE 2 study showed that patients treated with guselkumab experienced significant improvements in skin clearance and other measures of disease activity compared with placebo, and significantly greater improvements compared with the anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha treatment Humira (adalimumab). VOYAGE 2 is the second Phase III study to demonstrate superior efficacy of guselkumab versus adalimumab following VOYAGE 1.
Data from a third Phase III study (NAVIGATE) showed that patients who had an inadequate response following treatment with the anti-interleukin (IL)-12/23 monoclonal antibody (mAb) Stelara (ustekinumab) and who then switched to guselkumab, showed significantly greater improvements in skin clearance compared with patients who continued to receive Stelara.
In the VOYAGE 2 study, the co-primary endpoints were met at week 16, with 84.1 percent of patients receiving guselkumab 100 mg at weeks 0 and 4 and then every 8 weeks achieving an Investigator�s Global Assessment (IGA) score of cleared (0) or minimal (1) disease compared with 8.5 percent of patients receiving placebo (P < 0.001). In addition, 70.0 percent of patients receiving guselkumab achieved a Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) 90 score (near complete skin clearance) compared with 2.4 percent of patients receiving placebo (P < 0.001).Major secondary endpoints in VOYAGE 2 achieved statistical significance in comparisons of guselkumab versus adalimumab administered subcutaneously at weeks 0 (80 mg), 1 (40 mg) and then 40 mg every other week (all P < 0.001). At week 16, following three injections of guselkumab and ten injections of adalimumab, significantly higher proportions of patients receiving guselkumab versus adalimumab achieved IGA 0/1 (84.1 percent versus 67.7 percent, respectively) and PASI 90 (70.0 percent versus 46.8 percent, respectively). Guselkumab continued to demonstrate superiority versus adalimumab at week 24 for both the IGA 0/1 and PASI 90 scores. Among other secondary endpoints, significantly higher proportions of patients receiving guselkumab compared with adalimumab achieved Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores of 0/1 (indicating no impact of psoriasis on health-related quality of life) and PASI 100 scores (complete skin clearance) at week 24. Additionally, at week 16 and 24, 34.1 percent and 44.2 percent of patients receiving guselkumab achieved PASI 100 responses, respectively. Through week 16, the placebo-controlled period, 44.8 percent, 47.6 percent and 48.4 percent of patients receiving placebo, guselkumab and adalimumab, respectively, reported at least one adverse event (AE). Serious AEs were reported in 1.2 percent of patients receiving placebo, 1.6 percent of patients receiving guselkumab and 2.4 percent of patients receiving adalimumab.
NAVIGATE: Efficacy and safety of switching to guselkumab in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis patients with an inadequate response to Stelara.
The NAVIGATE study evaluated the efficacy and safety of guselkumab in patients who continued to experience mild to severe skin symptoms (IGA of 2 or more) following 16 weeks of treatment with Stelara. Patients who switched to guselkumab consistently showed greater improvement in their psoriasis between weeks 28 and 40, compared with patients who continued to receive Stelara, having twice as many office visits with at least a 2 point improvement in IGA from week 16, the study�s primary endpoint, and an IGA score of 0 or 1 (1.5 and 0.7 respectively; P < 0.001). Guselkumab also demonstrated superiority across major secondary endpoints in comparisons with Stelara. Major secondary endpoints included the number of visits that patients achieved a PASI 90 response or IGA score of 0 between weeks 28 and 40, and the proportions of patients that achieved an IGA score of 0 or 1 with at least a 2 point improvement from week 16 at week 28 (all P ? 0.001). In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients in the guselkumab group achieved an IGA score of 0 or 1 and at least a 2 point improvement from week 16 at week 52, and a PASI 90 response at weeks 28 and 52, compared with Stelara (all P < 0.001). Through week 60, AEs were reported in 64.4 percent of patients receiving guselkumab and 55.6 percent of patients receiving Stelara. Serious AEs were reported in 6.7 percent of patients receiving guselkumab and 4.5 percent in patients treated with Stelara, including 3 myocardial infarctions (2 from the guselkumab-treated group and 1 from the ustekinumab-treated group) and 2 malignancies (bladder carcinoma and a fatal squamous cell carcinoma of the neck, both in the guselkumab-treated group).
Results through week 48 for both the ongoing VOYAGE 1 and VOYAGE 2 studies were recently published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. Together with NAVIGATE, these three Phase III studies comprise the comprehensive clinical development program evaluating guselkumab in the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
See- "Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis with randomized withdrawal and retreatment: Results from the phase III, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator- controlled VOYAGE 2 trial." Kristian Reich, MD., et.al.-March 2017 Volume 76, Issue 3, Pages 418�431 .
See- "Efficacy and safety of guselkumab, an anti-interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody, compared with adalimumab for the continuous treatment of patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: Results from the phase III, double-blinded, placebo- and active comparator-controlled VOYAGE 1 trial." Andrew Blauvelt, MD, MBA, et. al., Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Vol. 76, Issue 3, p. 405�417.