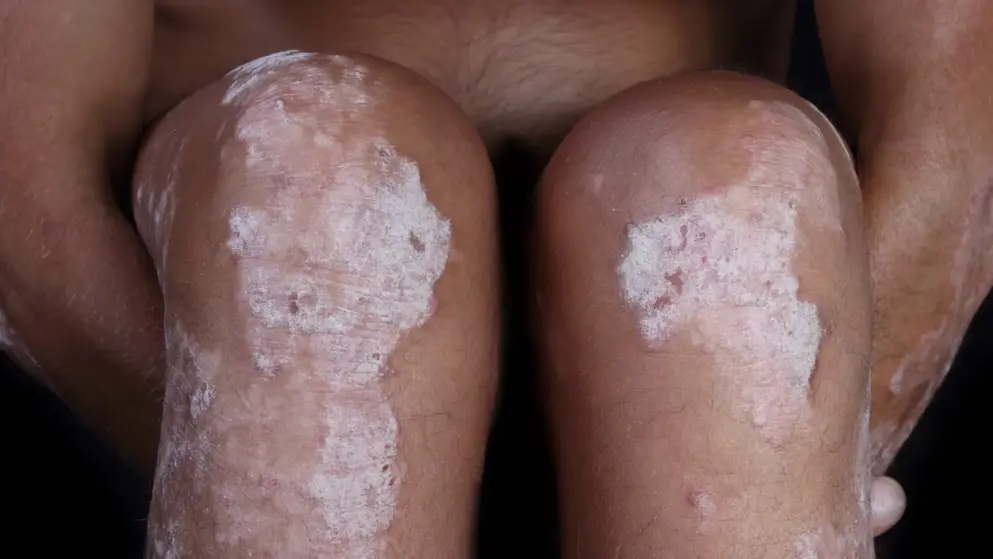
Phase III data on CNTO 1959 (guselkumab) in plaque psoriasis meets co-primary endpoints- Janssen
Janssen announced findings from the first of three pivotal Phase III studies evaluating CNTO 1959 (guselkumab), a subcutaneously administered anti-interleukin (IL)-23 monoclonal antibody in late-stage development for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Data from the VOYAGE 1 trial showed significantly higher proportions of patients receiving guselkumab achieved cleared/minimal disease compared with patients receiving placebo, as defined by at least a 90 percent improvement in the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI 90, near complete skin clearance) and an Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) score of cleared (0) or minimal disease (1) at week 16, the study co-primary endpoints.
The VOYAGE 1 trial also included an active comparator arm evaluating guselkumab versus Humira (adalimumab), and showed the superiority of guselkumab across major study endpoints and through 48 weeks of treatment. In the VOYAGE 1 study, the co-primary endpoints were met at week 16, with 85.1 percent of patients receiving guselkumab 100 mg at weeks 0 and 4 and then every eight weeks achieving cleared (IGA 0) or minimal disease (IGA 1) compared with 6.9 percent of patients receiving placebo. Nearly three-quarters of patients receiving guselkumab (73.3 percent) achieved a PASI 90 response, or near complete skin clearance, compared with 2.9 percent of patients receiving placebo. All major secondary endpoints in VOYAGE 1 achieved statistical significance in comparisons of guselkumab versus adalimumab administered subcutaneously at weeks 0 (80 mg), 1 (40 mg) and then 40 mg every other week.
At week 24, the proportion of patients who achieved a PASI 90 response was significantly higher in the guselkumab group compared with the adalimumab group (80.2 percent vs. 53.0 percent, respectively). Higher levels of skin clearance among the guselkumab group continued through weeks 24 and 48, with significantly more patients receiving guselkumab achieving IGA 0/1 and PASI 90, as well as measures of full skin clearance, as indicated by a 100 percent improvement in PASI score (PASI 100) or an IGA score of 0, compared with adalimumab. These data were presented at the 25th European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Congress and mark the first-ever results from a head-to-head study of an IL-23�targeted biologic therapy (guselkumab) compared with an anti-TNF-alpha treatment (adalimumab).